Ganges River Countries: Discovering The Rich Tapestry Of Nations Along The Sacred River
The Ganges River, one of the most sacred and significant waterways in the world, traverses through multiple countries, weaving together a rich cultural, historical, and ecological tapestry. Known as "Ganga" in India, this mighty river has been a lifeline for millions of people for centuries. Its journey spans across diverse landscapes, fostering life, culture, and spirituality. In this article, we will delve into the countries touched by the Ganges River, exploring their unique characteristics and the profound impact the river has on their people and environment.
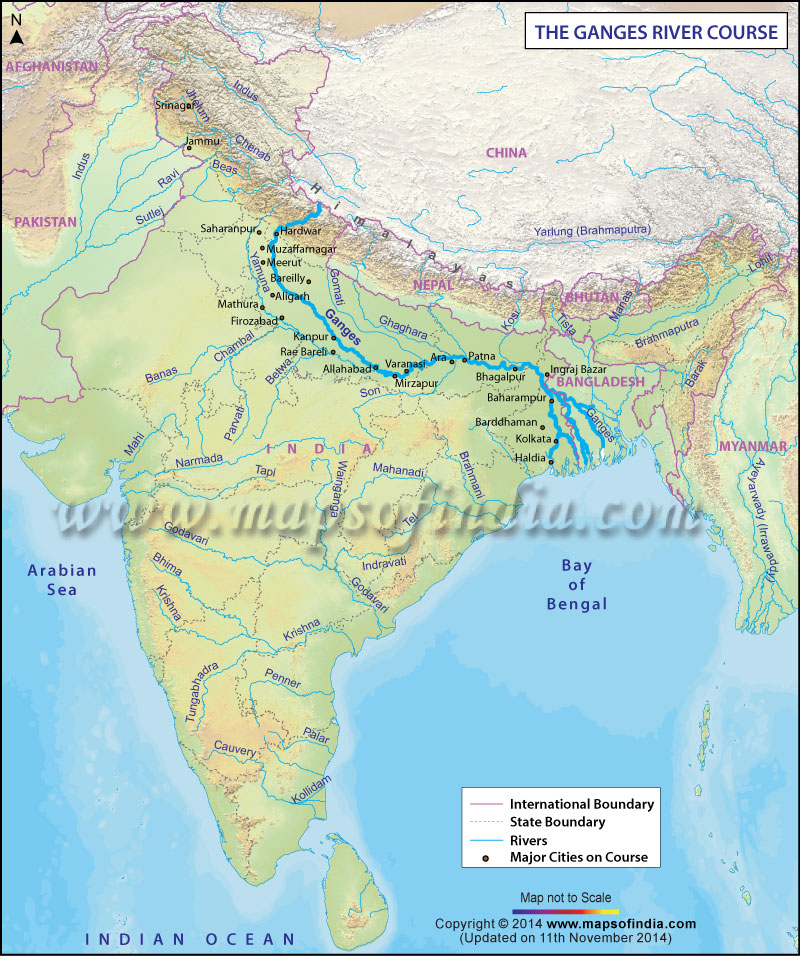
The Ganges River is not merely a geographical feature; it is a symbol of life, faith, and resilience. From its origin in the Himalayas to its confluence with the Bay of Bengal, it passes through countries that have been shaped by its waters. Understanding the relationship between the Ganges River countries is essential to comprehending the broader geopolitical and environmental dynamics of South Asia.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the Ganges River countries, highlighting their historical connections, cultural significance, and contemporary challenges. Whether you are a geography enthusiast, a student of history, or simply curious about the world's great rivers, this exploration will enrich your understanding of the Ganges and its role in shaping nations.
- Get Somali Telegram Links Top Channels And Groups You Need To Know
- Jill Wagner Accident Latest Updates News A Closer Look At The Story
Table of Contents
- Origin and Significance of the Ganges River
- India: The Heart of the Ganges River
- Bangladesh: The Delta Nation
- Nepal: The Upstream Guardian
- Geopolitical Dynamics of Ganges River Countries
- Cultural Impact of the Ganges River
- Environmental Challenges Faced by Ganges River Countries
- Economic Importance of the Ganges River
- Tourism Potential Along the Ganges River
- Conclusion: The Future of Ganges River Countries
Origin and Significance of the Ganges River
The Ganges River originates in the Gangotri Glacier, nestled in the lofty Himalayan mountains. Its journey spans over 2,500 kilometers, making it one of the longest rivers in Asia. This sacred river holds immense significance for millions of Hindus, who consider it a goddess and a source of spiritual purification. The Ganges River countries benefit immensely from its waters, which are used for irrigation, transportation, and industrial purposes.
Historical Importance
Historically, the Ganges River has been the cradle of ancient civilizations, including the Indus Valley Civilization. It has witnessed the rise and fall of empires, serving as a vital trade route and cultural hub. The river's waters have nourished fertile plains, enabling agriculture to thrive and supporting large populations.
Religious Significance
For Hindus, the Ganges River is not just a natural resource but a divine entity. Pilgrimages to cities like Varanasi and Haridwar, which are located along the river, are considered sacred. Bathing in the Ganges is believed to cleanse sins and bring salvation. This deep-rooted faith has shaped the cultural identity of the Ganges River countries.
- Secrets Of Sone 274 The Hidden Marvel You Need To Discover
- Shocking Odisha Mms Video Goes Viral Latest Scandal Unveiled
India: The Heart of the Ganges River
India is the primary country through which the Ganges River flows, covering a significant portion of its length. The river is central to the country's cultural, religious, and economic life. From the bustling cities to the serene countryside, the Ganges touches the lives of millions of Indians.
Key Cities Along the Ganges
- Varanasi: Known as the spiritual capital of India, Varanasi is a city of immense religious significance. It attracts pilgrims from all over the world who come to perform rituals and seek blessings.
- Haridwar: Located at the foothills of the Himalayas, Haridwar is another important pilgrimage site. It is here that the Ganges enters the plains, marking the beginning of its journey through India.
- Kolkata: As the river reaches its delta, Kolkata emerges as a major port city, leveraging the river's strategic location for trade and commerce.
Bangladesh: The Delta Nation
Bangladesh, located downstream of the Ganges River, is heavily influenced by its waters. The river forms a vast delta system in the country, creating fertile lands and supporting diverse ecosystems. The Ganges River countries, including Bangladesh, rely on the river for agriculture, fishing, and transportation.
Environmental Impact
The deltaic region of Bangladesh is prone to flooding, which can be both a blessing and a curse. While floods enrich the soil with nutrients, they also cause destruction and displacement. Efforts to manage the river's flow and mitigate its adverse effects are ongoing priorities for the government and international organizations.
Nepal: The Upstream Guardian
Nepal, nestled in the Himalayas, plays a crucial role as the upstream guardian of the Ganges River. The country's mountains feed the river with glacial meltwater, ensuring a steady flow throughout the year. Nepal's cooperation with downstream Ganges River countries is vital for sustainable water management.
Challenges in Water Management
Despite its strategic position, Nepal faces challenges in managing its water resources. Issues such as deforestation, climate change, and infrastructure development pose threats to the river's health. Collaborative efforts with neighboring countries are necessary to address these challenges effectively.
Geopolitical Dynamics of Ganges River Countries
The Ganges River countries share a complex geopolitical relationship, influenced by their dependence on the river's waters. Water-sharing agreements and diplomatic negotiations are essential to ensure equitable distribution and sustainable use of the river's resources.
India-Bangladesh Water Treaty
The India-Bangladesh Water Treaty, signed in 1996, is a landmark agreement that governs the sharing of Ganges River waters. It outlines the principles of cooperation and mutual benefit, setting a precedent for future negotiations between Ganges River countries.
Cultural Impact of the Ganges River
The Ganges River has profoundly influenced the culture and traditions of the countries it flows through. From religious festivals to art and literature, the river's presence is felt in every aspect of life. The cultural exchange between Ganges River countries has fostered a sense of unity and shared heritage.
Festivals Celebrating the Ganges
- Kumbh Mela: One of the largest religious gatherings in the world, Kumbh Mela is held at the banks of the Ganges in cities like Prayagraj and Haridwar.
- Ganga Dussehra: This festival celebrates the descent of the Ganges from heaven to earth, marking the river's divine origins.
Environmental Challenges Faced by Ganges River Countries
The Ganges River faces numerous environmental challenges, including pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change. Addressing these issues requires concerted efforts from all Ganges River countries and international partners.
Pollution Control Measures
Efforts to clean the Ganges River have gained momentum in recent years, with initiatives like the Namami Gange Programme in India. These programs aim to reduce industrial and domestic pollution, restore aquatic life, and improve the overall health of the river.
Economic Importance of the Ganges River
The Ganges River is a lifeline for the economies of the countries it flows through. It supports agriculture, fishing, transportation, and tourism, contributing significantly to their GDP. The river's resources are vital for the livelihoods of millions of people.
Agriculture and Irrigation
The fertile plains irrigated by the Ganges River are some of the most productive agricultural regions in the world. Crops such as rice, wheat, and sugarcane thrive in these areas, ensuring food security for the region's population.
Tourism Potential Along the Ganges River
The Ganges River offers immense potential for tourism, attracting visitors from around the globe. Its cultural and natural attractions make it a destination of choice for those seeking adventure, spirituality, and relaxation.
Popular Tourist Destinations
- Rishikesh: Known as the "Yoga Capital of the World," Rishikesh offers a unique blend of spirituality and adventure.
- Sundarbans: Located in the delta region, the Sundarbans is a UNESCO World Heritage Site renowned for its mangrove forests and wildlife.
Conclusion: The Future of Ganges River Countries
The Ganges River countries share a common destiny, tied together by the mighty river that flows through their lands. From its spiritual significance to its economic importance, the Ganges plays a pivotal role in shaping the lives of millions. As challenges such as pollution and climate change loom large, it is imperative for these countries to work together to protect and preserve this invaluable resource.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences about the Ganges River in the comments below. Explore more articles on our website to deepen your understanding of the world's great rivers and their impact on humanity.
Article Recommendations
- Victor Reynolds Train Accident Update Latest Developments And Insights
- Revealing Facts About Aditi Mistry Nude Videos Unveiling The Truth

Detail Author:
- Name : Ms. Lacy Williamson Sr.
- Username : janis98
- Email : rodger70@breitenberg.org
- Birthdate : 1973-07-07
- Address : 429 Lehner Alley Apt. 552 Stehrview, RI 57627-5556
- Phone : +12767927234
- Company : Hill-Lynch
- Job : Social Sciences Teacher
- Bio : Voluptatem voluptate voluptatem aut maiores consectetur vel odit. Est minus et aliquid consequatur quam. Dolorem impedit commodi quos enim distinctio est consequatur ducimus.
Socials
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/johnston1996
- username : johnston1996
- bio : Doloremque deleniti voluptatem sunt est ab illo.
- followers : 2407
- following : 936
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@justen.johnston
- username : justen.johnston
- bio : Est nemo doloribus qui adipisci eum ut.
- followers : 3186
- following : 1181
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/justen_johnston
- username : justen_johnston
- bio : Vel a molestiae voluptas amet.
- followers : 3797
- following : 2355
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/justen_johnston
- username : justen_johnston
- bio : Laboriosam quia quae doloribus natus consectetur. Officia recusandae quis consectetur necessitatibus sed. Delectus molestiae dolor eos cum ad similique ut.
- followers : 4643
- following : 1181